Speed Duo Leish K/Ehrli
Rapid combined detection of anti-Leishmania infantum and anti-Ehrlichia canis antibodies
| Presentation | Advantages | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
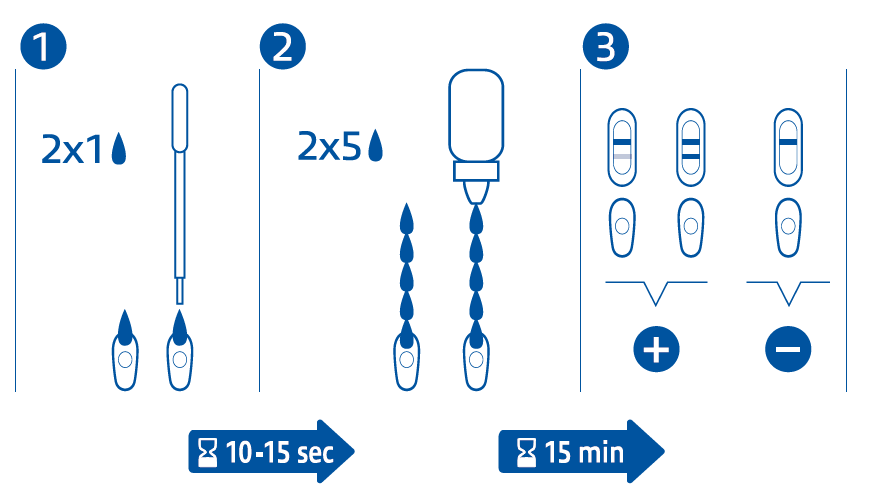
Method: Membrane Immunochromatography Analysis: Detection of anti Ehrlichia canis antibodies and of circulating antibodies (lgG) directed against Leishmania infantum Sample: Whole blood with anticoagulant, serum or plasma Preparation: 2 minutes Reading: 15 minutes Storage: 24 months at room temperature (2°C to 30°C) Presentations: 6 tests, 20 tests Reliability:
|
|
| Why to use Speed Duo Leish K/Ehrli ? |
|---|
|
Canine Ehrlichiosis is due to the infection of the animal's monocytes by a bacteria: Ehrlichia canis. After an acute stage, most often unnoticed, Depending on the region, seroprevalence in dogs varies from 0% to 60%. In endemic areas, as the Mediterranean basin, 25 to 30% of carriers are asymptomatic(4); ehrlichiosis is also highly prevalent (4). Coinfections are common and differential diagnosis is difficult. For either of the 2 diseases, the detection of circulating antibodies by immunochromatographie is more sensitive than the direct highlighting of the parasite. |
| When to use Speed Duo Leish K/Ehrli ? |
|---|
|
In the presence of suggestive symptoms, Speed Duo Leish/Ehrli can be used to clarify the etiological diagnosis and to help the practitioner with the differential diagnosis. In endemic areas, using Speed Duo Leish/Ehrli regularly is strongly recommended to enable early detection of the diseases in asymptomatic dogs (3). Returning from an endemic area, Speed Duo Leish/Ehrli can be used to screen for a potential seroconversion |
Instructions for use
Bibliography
(1) BOURDOISEAU G. Parasitologie clinique du chien. 2000, Ed. NEVA, 325-362
(2) BIANCHI D. Evaluation d'un nouveau kit commercial Speed LeishTM destiné au diagnostic de la Leishmaniose, Thèse Med Vet Lyon 2001
(3) GREVOT A. Etude comparative de différents tests de diagnostic rapide de la Leishmaniose Canine, Thèse Med Vet Lyon 2001
(4) TROTZ-WILLIAMS L.A., TREES A.J. Systematic review of the distribution of the major vector-borne parasitic infections in dogs and cats in Europe. Vet Record, 2003, 152, 97-105

 Canine Leishmaniosis is due to the proliferation in the macrophages of Leishmania infantum. The clinical phase of the disease precents an asymptomatique stage that lasts from a few months to years (1 ). The disease is transmitted by sand flies: the phlebotomes.
Canine Leishmaniosis is due to the proliferation in the macrophages of Leishmania infantum. The clinical phase of the disease precents an asymptomatique stage that lasts from a few months to years (1 ). The disease is transmitted by sand flies: the phlebotomes. illness evolves towards a long subclinical stage of several months. The vector of Ehrlichia is a tick: Rhipicephalus sanguineus.
illness evolves towards a long subclinical stage of several months. The vector of Ehrlichia is a tick: Rhipicephalus sanguineus.